Setting up and running B2B Customer Experience (CX) programmes is our ‘bread and butter’ at Deep-Insight.
We’re used to handling questions on how to make CX programmes more effective. One of the most common questions we get from first-time clients is: “What completion rates can I expect from my CX programme?” Another common question from longer-term clients is “How do I improve my completion rates?”
Let’s deal with each question in turn.
“What Completion Rates can I expect from my CX programme?”
Let me preface this by saying that we are talking about business-to-business (B2B) relationships so there is an inherent assumption in the question that our clients have some existing – and hopefully strong – relationships with their customers and that these contacts will be receptive to a request to give feedback as part of that ongoing relationship.
This is usually the case but clients – particularly senior clients – are busy people so it may not come as a surprise to hear that the average participation rate in a B2B customer assessment is around 35%.
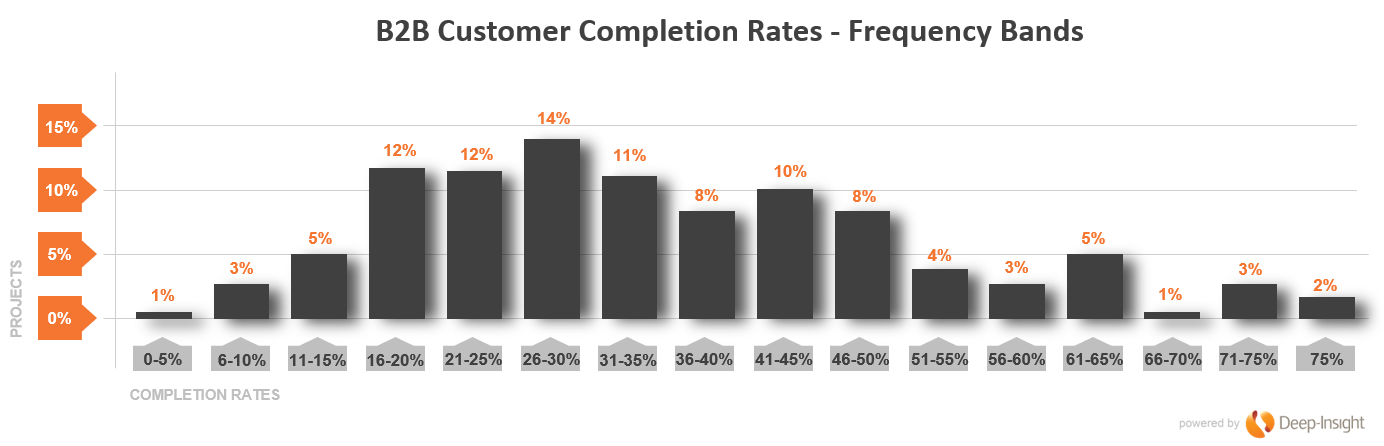
But that 35% figure is an aggregate score and there’s a little more to it than that, if you have a look at the graph below.
The spread is wide.
The most common completion rate is in the 26-30% range. We have a smaller number of clients – typically those who have been running our Customer Relationship Quality (CRQ) assessments for many years – who regularly achieve completion rates of 50% and higher.
If this is your first time running a customer assessment – either a simple Net Promoter Score survey of something a little more complex like our CRQ relationship assessments – you can expect completion rates of less than 1 in 3.
This may sound OK if you regularly run consumer surveys where a 5% completion rate can be a good result, but for an existing long-standing B2B client relationship, it’s paltry. And yet we have been running customer assessments of all sorts for nearly 20 years and these are the actual numbers.
So now let’s get to the second question:
“How do I improve my completion rates?”
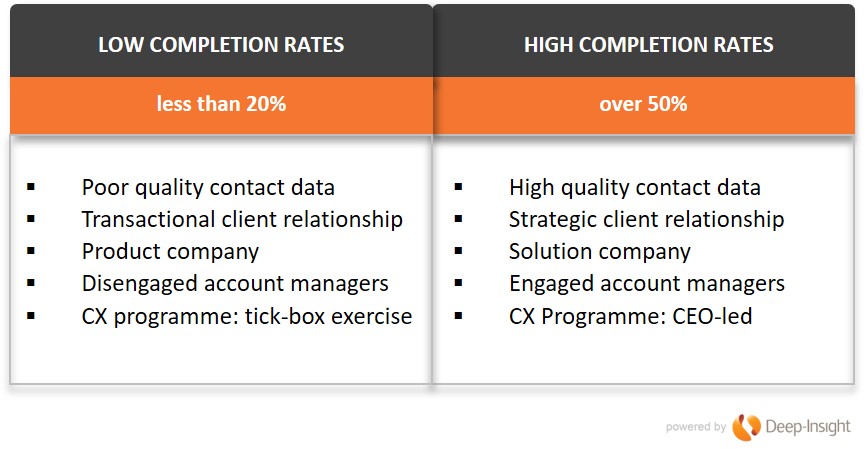
The starting point is to understand why some B2B companies sometimes get really low completion rates and others consistently exceed 50%.
Our lowest-ever completion rate (4%) came from a first-time UK software client. The quality of contact data was simply terrible. We should have spotted that it was little more than a ‘data dump’ from the company’s CRM system. The list included people who had left their companies three years earlier. It included people who had never even heard of our client. It probably included the names of people who were dead. That’s because there was no governance in place for the programme. The Sales Director was not involved. Account Managers did not personally sign off the client contact names. You get the picture.
Our highest-ever completion rate came from a company that has been a client of Deep-Insight’s for 10 years and whose customers view the annual CRQ assessment as a critical part of their ongoing strategic partnership.
But there are other reasons for low and high participation rates. Here’s a quick summary of the profiles of our clients that fit into both categories:
6 Steps to Improve your Completion Rates
Here are the steps you need to take to get your completion rates up:
- Make It Strategic. If the CX programme is CEO-led and driven from the top, it will not be seen as another box-ticking exercise. Make sure this is a key item on the Executive agenda.
- Put in Governance Structures. By this we mean things like: a) Account Directors should supervise and sign all contact names, not just pull them from the CRM system; b) the Sales Director should personally sign off all Strategic Client contact names.
- Don’t call it a Survey! At Deep-Insight, we ban the use of the term “survey” . For us, a CRQ assessment is a strategic ongoing conversation with the clients and their views will be taken seriously.
- “Warm Up” the Contacts. An invitation to complete a survey should not come out of the blue. Ideally, it should be introduced by letter or by email by the CEO or Country Manager, and while an assessment is “live”, the account manager will know to stay in touch with the client and urge them to complete the assessment.
- Close the Loop. This is critical. If you ask for feedback, you need to share that feedback with the client, agree the actions that BOTH PARTIES will take to improve the relationship.
- Repeat. Get into a rhythm where your clients and your sales/account teams know that every February or October (or whenever), the annual strategic assessment will take place. You may want to run frequent assessments. Some companies have quarterly Net Promoter or Pulse assessments – but don’t overdo the frequency. Your organisation needs time to put remedial actions into effect.
Completion Rates of 90% or more?
Follow the above steps and you’ll get your completion rates to 50% or higher.
But remember that these completion rates are at an individual level. You should be getting feedback from multiple people at different levels within each client. Include Influencers and Operational Contacts as well as Key Decision Makers. That way you’ll get a wealth of information about what your key accounts REALLY think of you.
You’ll also get completion rates of 90% at an account level if you take this approach.
If you are interested in reading more about running a CX programme effectively take a look at our process for running a B2B CX assessment or just get in touch with us today for a chat.